 The Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Nirmala Sitharaman, presented the Union Budget 2026-27 in Parliament, marking the first budget prepared in Kartavya Bhawan. The budget is inspired by three Kartavyas: accelerating and sustaining economic growth, fulfilling the aspirations of citizens and building their capacities, and promoting inclusive development in line with the vision of Sabka Sath, Sabka Vikas. Emphasizing a Yuva Shakti-driven approach, the government reaffirmed its focus on the poor, underprivileged, and disadvantaged, while steering India towards a Viksit Bharat with balanced ambition and inclusion.
The Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Nirmala Sitharaman, presented the Union Budget 2026-27 in Parliament, marking the first budget prepared in Kartavya Bhawan. The budget is inspired by three Kartavyas: accelerating and sustaining economic growth, fulfilling the aspirations of citizens and building their capacities, and promoting inclusive development in line with the vision of Sabka Sath, Sabka Vikas. Emphasizing a Yuva Shakti-driven approach, the government reaffirmed its focus on the poor, underprivileged, and disadvantaged, while steering India towards a Viksit Bharat with balanced ambition and inclusion.
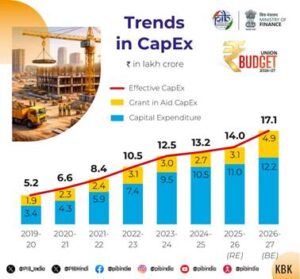
To sustain economic growth, the budget proposes interventions across multiple sectors. Public capital expenditure is set to increase from ₹11.2 lakh crore in BE 2025-26 to ₹12.2 lakh crore in FY 2026-27. Seven high-speed rail corridors will be developed as “growth connectors,” along with expansion of Dedicated Freight Corridors and 20 new National Waterways over the next five years to enhance sustainable transport. The government also plans to map City Economic Regions (CERs) and allocate ₹5,000 crore over five years to implement city-specific growth plans through a challenge-based financing model.
The budget lays strong emphasis on industry and innovation. The Biopharma Shakti initiative, with an outlay of ₹10,000 crore, aims to establish India as a global hub for biologics and biosimilars. A ₹10,000 crore SME Growth Fund is proposed to create future “Champion MSMEs.” The textile sector will be modernized and strengthened through programs supporting natural and man-made fibres, traditional clusters, and skilling initiatives. Technology and creative sectors also receive a boost, with AVGC Content Creator Labs to be set up in 15,000 secondary schools and 500 colleges.
Education, skills, and healthcare remain a priority. The government plans to establish one girls’ hostel per district in STEM institutions and launch a National Institute of Hospitality to bridge academia, industry, and governance. Five Regional Medical Hubs are proposed to enhance medical tourism and healthcare employment. For the veterinary sector, capital subsidies will support new colleges, hospitals, and diagnostic facilities. The Khelo India Mission aims to systematically transform the sports ecosystem over the next decade.
On agriculture and rural development, the budget introduces Bharat-VISTAAR, a multilingual AI tool integrating AgriStack portals and ICAR packages to provide farmers with better advisories and productivity support. Community-led Self-Help Entrepreneur (SHE) Marts will empower women entrepreneurs, while targeted initiatives will focus on industrial and tourism development in the Purvodaya states and North-East.
The direct tax reforms include the rollout of the New Income Tax Act, 2025 from April 2026, simplified compliance forms, and rationalized penalties and prosecution processes. Tax incentives for cooperatives, IT services, and non-resident foreign investors are proposed to strengthen domestic enterprise and attract global investment. In particular, foreign cloud service providers will enjoy a tax holiday until 2047, while safe harbour provisions for IT services have been made more accessible.
On the indirect tax front, customs duties have been rationalized to support domestic manufacturing and exports. The budget proposes reduced duties for capital goods used in lithium-ion cell production, critical mineral processing, and medical drugs. Customs warehousing is being transformed into a warehouse operator-centric system with self-declarations and electronic tracking, while cargo clearance processes are being streamlined through a single, integrated digital platform.
Fiscal consolidation is a key highlight, with the debt-to-GDP ratio projected at 55.6% and the fiscal deficit at 4.3% of GDP. Net tax receipts are estimated at ₹28.7 lakh crore against total expenditure of ₹53.5 lakh crore. The budget also emphasizes leveraging technology, AI, and global partnerships to boost competitiveness, infrastructure, and human capital.
In summary, the Union Budget 2026-27 combines economic growth, social inclusion, and technological innovation. Through targeted investments in infrastructure, industry, education, healthcare, and agriculture, the government aims to empower citizens, strengthen domestic manufacturing, attract global investment, and build a resilient, inclusive economy for a Viksit Bharat.


